Worms or helminths are parasites that live, feed, grow and reproduce in the human body, in other words, use it to carry out their life cycle. According to various statistics, there are between 300 and 500 species of worms in the world that are dangerous to humans. Their prevalence varies by country and depends on the level of hygiene culture of the population and the socio-economic development of the region. But even in enlightened European countries, symptoms of helminthiasis are found in a third of the population. Worm larvae can enter the human body in different ways, depending on their development cycle. The names of worms in humans, their types, as well as methods of infection, symptoms and methods of treating helminthiasis are relevant information for the majority of the world's population.
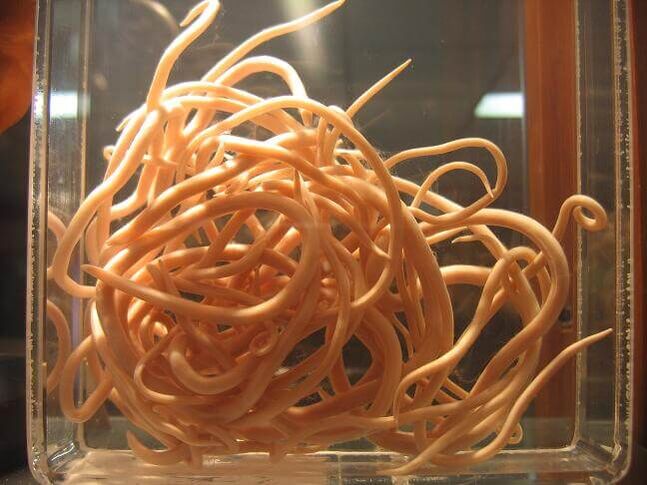

What types of worms are there?
Over the years of evolution, parasites have adapted ideally to live at the expense of other living things, without raising suspicion in the immune system for a long time, so the symptoms of worms in humans do not appear immediately, and may not be present at all ora little. expressed.
Worms are able to penetrate the body unnoticed, disguise themselves, destroy tissues and organs, and poison the human body with toxins, staying in it for a long time.
Some types of worms are only harmful to humans, while others are parasitic on animals. They vary in size from microscopic to gigantic (15 or more meters long). About three dozen parasites are common, including single-celled protozoa. Among all the diversity, there are 3 main groups of helminths depending on the characteristics of their life cycle:
- Contact the worm- found only in humans, has a simple developmental cycle that does not require more than one host. Common representatives are pinworms; this is the most common intestinal worm in children. Infection occurs in families, groups of children, public places through unwashed hands, household items (toys, books, curtains, etc. ) where mature eggs of this worm have fallen, as well as through dust inhalation.
- Group of geohelminths– their eggs must first mature in soil, water or sand. They enter the human body through the mouth with unwashed berries, vegetables or herbs (such as roundworms and whipworms) or through the skin (such as hookworms).
- Biohelminths– has a complex life cycle with host changes. These worms appear in humans by eating vegetables or raw water that is not properly washed (echinococcus), animal meat contaminated with larvae (beef or pig tapeworms), planned fish and caviar (broad tapeworms), river fish (fluke or liver fluke) or through the bloodstream. (filaria).
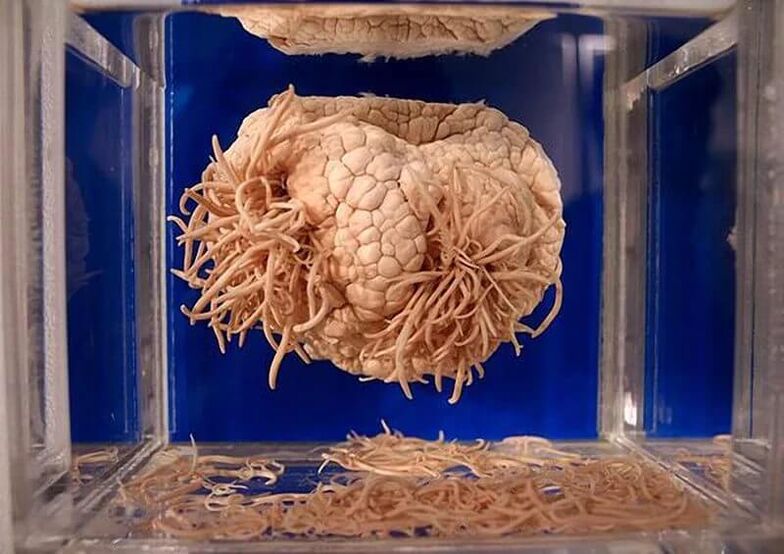
Types of worms
All types of helminths are divided into 3 classes according to morphological characteristics:
- Class nematodes (roundworms)– roundworms, pinworms, hookworms, whipworms, trichinella. Roundworms are distinguished by the presence of separate sexes and have different sizes - from 1 cm (female pinworm) to 40 cm (ascaris).
- Class trematodes (commonly called flukes)– Siberian fluke (cat fluke), schistosomes. They are always biohelminths and hermaphrodites, equipped with various devices for suction and attachment to a person's internal organs.
- Class cestodes (types of flatworms)- This is a long tape parasite. These include broad tapeworms, pork and beef tapeworms - these are the largest worms, capable of growing up to 20 meters in length. Flatworms eat the entire surface of the body, are hermaphrodites and biohelminths. Echinococcus is considered the smallest representative of cestodes.
What the world of worms is all about is great diversity and incredible survival. The classes of trematodes and cestodes are 100% parasitic, but roundworms are heterogeneous, there are several tens of thousands of species, but not everyone likes to parasitize the human body. Most helminths lay eggs that can survive in the external environment for several months, and Trichinella is a viviparous individual..
In the human body, worms not only live in the intestines, but some of them prefer to be located in the liver, lung parenchyma, brain, skin, muscle tissue and even in the eyeball.
Worms can live a long time; for example, cysticercus can live in the brain for years; Hydatid cyst growth continues for up to 10 years.
About roundworms
What are the most common worms:
- pinworms- lives in the lower part of the small intestine and throughout the large intestine of humans; females lay eggs around the anus at night, causing the characteristic sign of enterobiasis in humans - itching. Transmission of worms between humans occurs through dirty hands (eggs of these worms under children's nails are very often found), bedding, and household items. Eggs are very light and can be transmitted through the air with dust; it remains viable for up to six months. This is the least toxic worm. Human feces do not contain them; for diagnosis it is necessary to take a scraping from the perianal area.
- Ascaris- a large worm with a curved hook-shaped tip; mature individuals can reach a length of up to half a meter. Eggs ripen in the soil and enter the stomach and small intestine with unwashed berries, vegetables or herbs. The released larvae gnaw the intestinal wall, penetrate the hepatic vein, from there, with the blood flow, they rush to the lungs, the right side of the heart, sometimes to the brain and eyes, and inflammation develops in these organs. When coughing, sputum with larvae enters the mouth and is re-swallowed into the gastrointestinal tract, where mature individuals develop, laying eggs after a month. These worms are brown or reddish in color because they seize red blood cells. The lifespan of roundworms is up to 2 years. For diagnosis, stool is tested for worm eggs.
- whipworm- a hair-thin worm, about 5 cm long with a pointed tip, with which it attaches to the inner surface of the intestinal wall. Eggs mature in the soil, from where they penetrate into the intestines, and larvae appear here. Whipworms feed on blood and like to live in the cecum and appendix, often causing inflammation and anemia. The lifespan is about 3-4 years. To detect it, you need to test your stool for worm eggs.
- Trichinella- small roundworms that move between predators and prey. A person becomes infected by eating meat with larvae; in the intestine, after a few days, mature individuals of Trichinella are formed, which then give birth to live larvae. Through the blood they can infect the whole body, but they prefer the skeletal muscles, where they remain for up to 5 years.
About tapeworms and worms
What types of worms cause the greatest harm to the human body:
- Bovine tapeworm (commonly called tapeworm)- considered to be the largest worm in humans (up to 15-20 meters) with a body in the form of a ribbon of thousands of individual segments, among which the most mature is in the tail and falls when the eggs inside mature. These fragments are the size of a human fingernail, they fall to the ground, grass, and then end up in the cow's body. A person becomes infected through beef. Bovine tapeworms can live in a person's small intestine for up to 10 years; it consumed the entire surface of his body. For diagnosis, stool is examined.
- Pork tapeworm– similar to the bull tapeworm, but shorter in length. If a person is infected with larvae, tapeworms grow in the small intestine; when the eggs are infected, the larvae migrate and can infect any organ.
- Wide tapeworm– their type of worm is flat, more than 12 meters long. A person becomes infected by eating undersalted caviar, dried or undercooked fish. It can reside in the small intestine for decades, constantly releasing mature segments with larvae into the environment.
- Echinococcus- the smallest parasite of the class cestodes. For several years, the larvae form cysts, which can be located in different organs and reach a diameter of 10 cm or more. Infection occurs from sick dogs or livestock. This course is characterized by a clear clinical picture and risk of complications.
- Cat fluke (liver).- small worms that enter the human body by eating poorly cooked freshwater fish, live in the lumen of the small intestine, in the bile and pancreatic ducts, can multiply quickly and live up to two decades.
Despite the wide variety of species, it is possible to determine exactly which worms live in the human body using modern diagnostic methods and an old proven test - feces for helminth eggs.
Treatment is carried out after confirmation of the diagnosis and prescription of the attending physician.






































